Adware In Real World and Its Impacts
Computer users frequently experience both the advantages and drawbacks of the digital age in a time when technology is the foundation of our daily lives. A persistent annoyance that can ruin your online experience and jeopardize the security of your computer is adware. This article aims to provide you with direction as you travel through the adware jungle.
Quick Links
Adware, short for “advertising-supported software,” is a type of unwanted software that infiltrates your computer, bombarding you with intrusive advertisements. These advertisements, which include pop-ups and banners, not only impede your browsing experience but also have the potential to drastically reduce the speed of your computer.
A seamless online experience is not the only benefit of removing adware; your computer’s security and data privacy are also protected. Adware often comes hand in hand with risks like data theft and exposure to malicious content. Therefore, ridding your system of adware is paramount.
We’ll give you a step-by-step tutorial in this article on how to successfully remove adware from your computer. Whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast or a computer newbie, our all-encompassing approach will enable you to take charge of your digital space and ensure a safer, more enjoyable, and adware-free computing experience.
Understanding Adware

In the vast realm of digital threats, adware stands as a distinct but often misunderstood entity. To effectively combat it, one must first comprehend its nature and origins.
Adware, derived from “advertising-supported software,” is a category of potentially unwanted software (PUP) that plagues computer users with intrusive and often irrelevant advertisements. Unlike other types of malware like viruses or Trojans, adware typically doesn’t aim to directly harm your system or steal your data. Instead of posing a serious security risk, it aims to annoy you by over saturating your digital experience with advertisements.
Infiltration Tactics
Adware finds its way into your computer through various entry points. The most common method is software bundling, which piggybacks onto legitimate software installations. Users unwittingly invite adware when downloading free software, neglecting to uncheck optional adware installation boxes. Additionally, it may spread through misleading advertisements, malicious downloads, or by taking advantage of software flaws.
Adware developers are driven by financial gain. They frequently rely on pay-per-click (PPC) advertising models, which allow them to make money through ad impressions and clicks. Some adware adopts a more intrusive strategy by monitoring user information and online activity to produce targeted ads. This practice, also referred to as adware spyware, poses serious privacy issues. Users can better appreciate the significance of removing adware from their systems, safeguarding their digital privacy, and reclaiming a smoother online experience by comprehending these motivations.
Risks and Dangers of Adware
While adware may appear as a mere annoyance with its constant pop-up ads and browser disruptions, delving deeper reveals a host of risks and dangers that underscore the urgency of its removal.
1. Privacy Invasion

Adware, especially the more insidious variants, has a penchant for invading your privacy. Your online activity, including the websites you visit, the searches you conduct, and even the keys you press, are frequently tracked by tracking mechanisms. Your online privacy is then disturbed when this data is collected and shared with outside parties. Although the information gathered can be used to produce extremely targeted advertisements, it also raises questions about unauthorized access to your personal data.
2. Data Theft

Beyond privacy invasion, adware can escalate to outright data theft. Sensitive data, such as login credentials, credit card information, and personal identification, can be captured by some malicious adware strains. Your digital security and personal safety are seriously at risk because of the possibility that this stolen data will result in identity theft and financial losses.
3. Exposure to Malicious Content
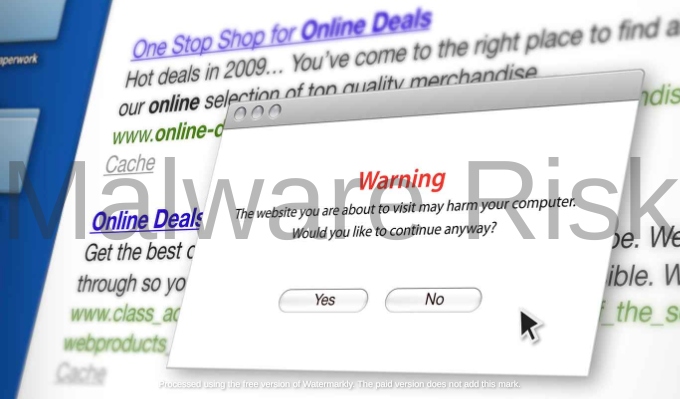
Adware doesn’t operate in isolation; it often opens the door to more malicious threats. Clicking on adware-generated ads or pop-ups can redirect you to websites laden with malware, including viruses, Trojans, and ransomware. These malicious payloads can exploit vulnerabilities in your system, leading to further compromise and potential damage to your computer and data.
4. System Instability

Adware can seriously harm your computer’s stability and performance. Your computer will slow down, freeze, or crash as a result of the constant barrage of ads consuming precious system resources. Your workflow will be disrupted by this performance decline, which, in more serious cases, could also result in data loss or corruption. Adware can deteriorate your system’s general health and functionality the longer it stays on it.
It’s critical to understand that the dangers posed by adware go far beyond mere inconvenience. They discuss issues related to system dependability, security, and privacy. Proactive measures are needed to address these risks, such as routine adware scans and efficient removal methods.
To help you regain control over your online life and protect your personal information, we’ll walk you through the process of locating and removing adware from your computer in the sections that follow.
Methods of Adware Infiltration
Adware employs a variety of cunning tactics to infiltrate computers, often capitalizing on unsuspecting users’ behaviors and vulnerabilities. Understanding these infiltration methods is crucial to bolstering your defenses against unwanted adware infections.
Software Bundling
One of the most common ways adware gains entries into computers is through software bundling. Adware developers partner with legitimate software providers to include their adware in the installation package of popular and free software. Users eager to download and install the desired software often overlook or fail to notice the checkboxes that allow adware installation. These bundled adware programs then piggyback into your system during the installation process.
Malicious Downloads
Adware can also sneak into your computer through malicious downloads. This typically occurs when users visit untrustworthy websites or engage in risky file-sharing practices. Downloading files, especially cracked software or media from dubious sources, can result in adware installation. Such downloads often come bundled with hidden adware payloads, ready to activate upon execution.
 Deceptive Ads and Fake Updates
Deceptive Ads and Fake Updates
Adware creators capitalize on users’ trust in online advertisements and software updates. Deceptive ads can mimic legitimate system alerts or notifications, urging users to click on them for essential updates or security scans. Clicking on these faux updates or ads can lead to adware installations, as users unknowingly grant permission for the intrusion. Adware can also disguise itself as fake software updates, tricking users into downloading and installing it under the guise of a beneficial upgrade.
Unintentional Invitations
Beyond these tactics, adware often takes advantage of unsafe online practices:
- Ignoring Installation Prompts: Rushing through software installations requires carefully reviewing the setup options to avoid unintended adware installations. Users should always opt for custom installations, which allow them to deselect optional bundled software.
- Clicking on Suspicious Links: Clicking on links embedded in unsolicited emails, dubious websites, or deceptive pop-ups can lead to adware downloads. Vigilance and scepticism when encountering such links can prevent inadvertent adware infections.
- Disabling Security Software: When antivirus or antimalware software is turned off or outdated, adware can take advantage of security flaws. To safeguard against adware and other threats, security software must be regularly updated and maintained.
Users can lessen their susceptibility to adware and maintain a more secure and adware-free computing environment by being aware of these infiltration techniques and implementing safe online practices. We will go into detail about how to effectively remove adware and stop new infections in the following sections.
Manual Removal of Adware
It can be rewarding to take control of your computer and get rid of adware, and you don’t always need outside software to do it. In this section, we’ll walk you through manually removing adware from Chrome, Firefox, and Edge, three widely used web browsers. Let’s begin.
Removing Adware from Google Chrome
Following are the steps you can follow to remove adware from your computer using Google Chrome:
1: Open Chrome and click on the three vertical dots in the top-right corner to access the menu.
2: Select “Settings” from the dropdown menu.
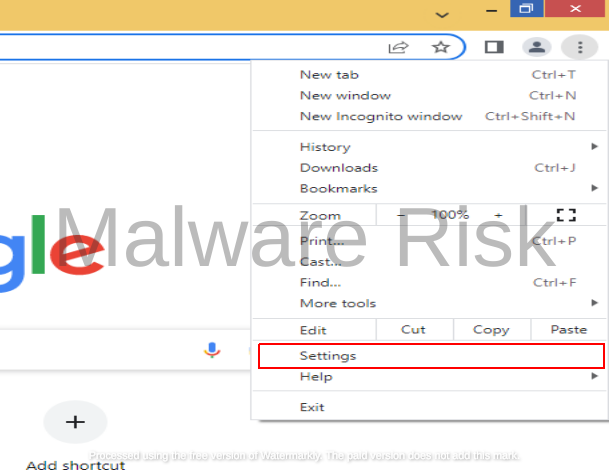
3: Navigate to the “Settings” page, scroll down, and click on “Site settings” under the “Privacy and Security” section.
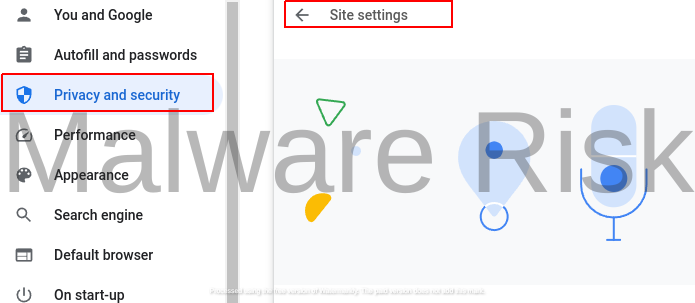
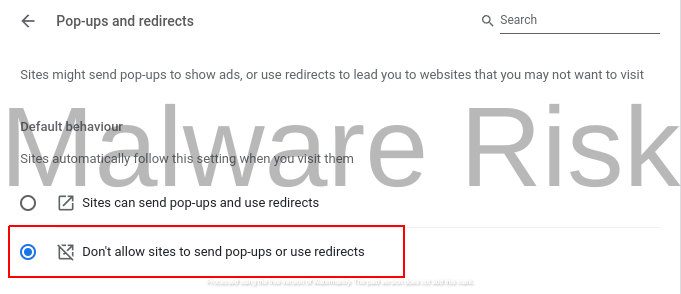
7: Select “Pop-ups and redirects” and choose “Don’t allow sites to send pop-ups or use redirects“.
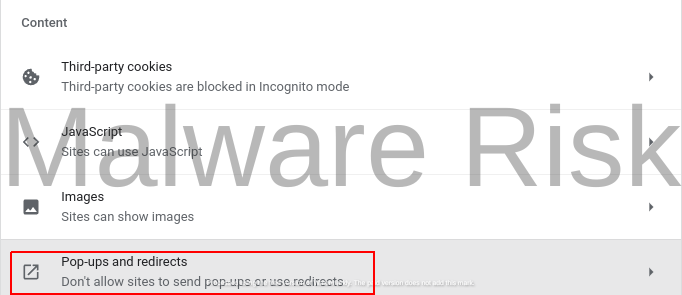
8: Go back to the “Settings” page and click on “Extensions” on the left sidebar. Remove any suspicious or unwanted extensions by clicking the “Remove” button below them.
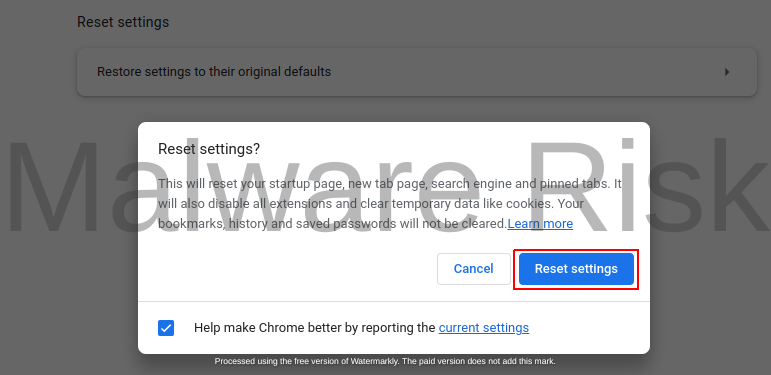
9: Scroll back up to the top of the “Settings” page, and under “Reset and clean up,” click on “Restore settings to their original defaults.” Confirm the reset.
So, it’s not a big deal to remove adware from your computer as long as the issue is not so big.
Removing Adware from Mozilla Firefox
Following are the steps you can follow to remove adware from your computer using Mozilla Firefox:
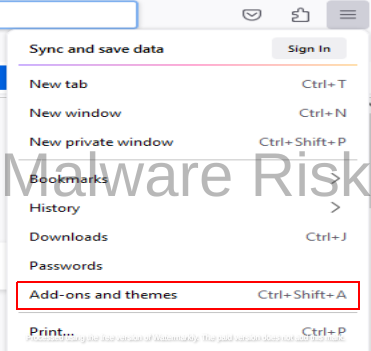
1: Open Firefox and click on the three horizontal lines in the top-right corner to access the menu.
2: Select “Add-ons and themes” from the dropdown menu.
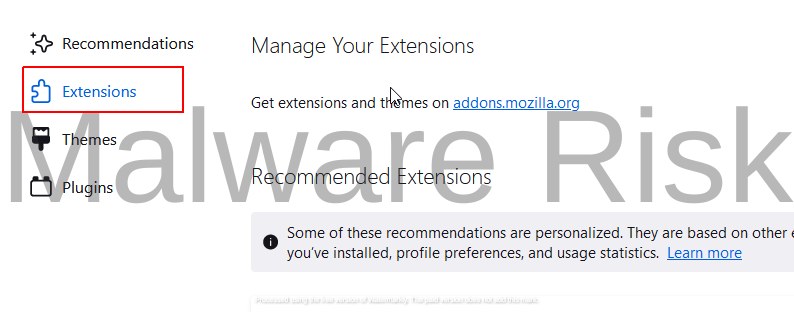
3: In the “Add-ons Manager“, navigate to the “Extensions” tab. Remove any unwanted or suspicious extensions by clicking the “Remove” button next to them.
4: Follow Step 1 again and choose “Help” then “More troubleshooting information” and click on “Refresh Firefox” button to reset the browser to defaults.
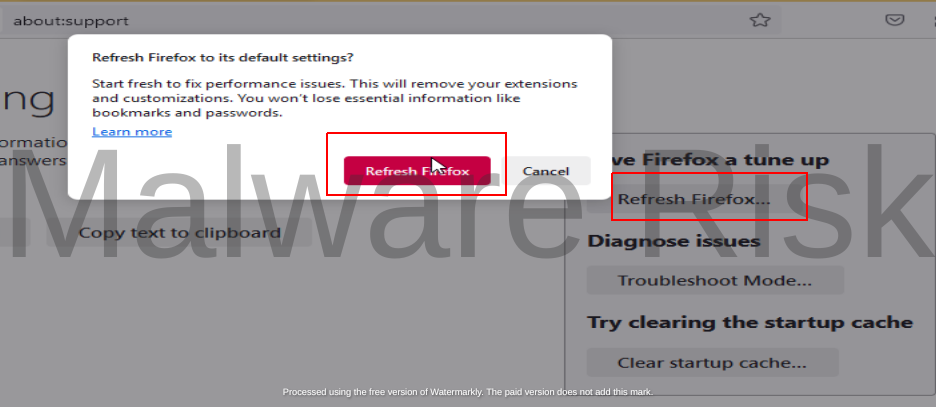
That’s how you can remove adware from your computer with ease.
Removing Adware from Microsoft Edge
Following are the steps you can follow to remove adware from your computer using Microsoft Edge:
1: Open Edge and click on the three horizontal dots in the top-right corner to access the menu.
2: Select “Extensions” from the dropdown menu.
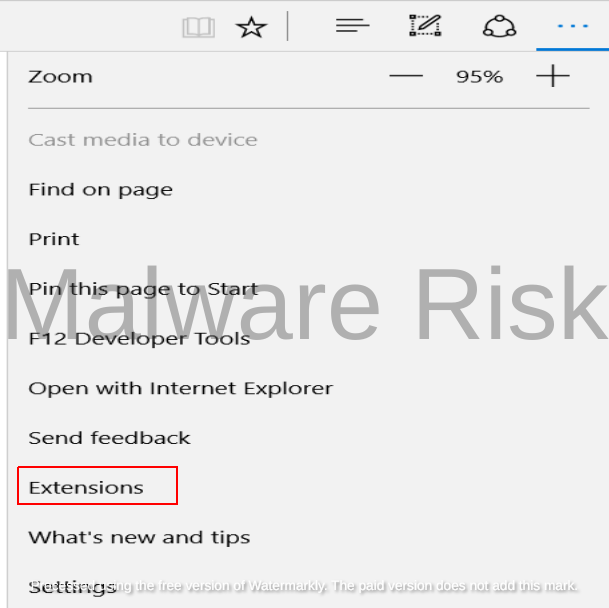
3: Locate any extensions you didn’t install or find suspicious and click “Remove” beneath them.
4: In the Edge menu, select “Settings.” Scroll down and click on “Reset settings” under “Reset and clean up.” Confirm the reset.

These exact steps and options may vary slightly based on browser versions. It’s essential to stay vigilant while removing adware manually and only remove extensions or make changes that you are confident are related to adware.
You can effectively remove adware from your system without using third-party software by following these instructions and regularly checking your browsers for suspicious extensions or settings. This hands-on approach ensures a cleaner, adware-free browsing experience and gives you more control over your computer’s security.
Preventing Adware Infections
Adware infections can be a recurring annoyance, but by taking proactive steps, you can greatly lower your risk of becoming a victim of these invasive intruders. Here is a detailed guide to avoiding adware infections and upholding a secure online setting.
1. Safe Browsing Habits
- Exercise Caution: Be discerning about the websites you visit. Avoid shady or suspicious websites that often harbor adware and other malware. Stick to reputable sources for downloading software and files.
- Ignore Unsolicited Emails: Phishing emails may contain links to malicious websites that can lead to adware infections. Refrain from clicking on links or downloading attachments from unsolicited or unknown senders.
- Use HTTPS: Whenever possible, access websites using HTTPS connections. Secure websites are less likely to host adware or other malicious content.
2. Avoiding Suspicious Downloads
- Download from Trusted Sources: Only download software, applications, and files from official websites or trusted sources. Avoid third-party download sites that may bundle legitimate software with adware.
- Read User Reviews: Before downloading any software, read user reviews and check for any reports of bundled adware. If many users report adware issues, consider alternative software.
- Uncheck Optional Offers: During software installations, carefully review all installation screens. Uncheck any boxes that offer to install additional software, as these often contain adware.
3. Keeping Software and Browsers Updated
- Enable Automatic Updates: Ensure that your operating system, web browsers, and all software are set to receive automatic updates. These updates often include security patches that can protect against adware vulnerabilities.
- Regularly Check for Updates: Occasionally, manually check for updates for your operating system, browsers, and installed software. Keeping everything up-to-date is crucial for security.
4. Using Ad-Blockers and Security Extensions
- Install Ad-Blockers: Consider using browser extensions or add-ons that block online advertisements. These can significantly reduce your exposure to adware-laden ads and pop-ups.
- Use Security Extensions: Install reputable security extensions or add-ons that provide real-time protection against malicious websites and downloads. These extensions can prevent adware from infiltrating your system.
- Enhance Browser Security: Many modern browsers offer enhanced security features. Enable features like sandboxing and phishing protection to bolster your defense against adware.
Following these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of adware infections and maintain a secure and hassle-free computing experience. Remember that vigilance and safe online practices are your best defense against adware and other digital threats.
Cleaning Up After an Infection
Successfully removing adware from your computer is a significant victory for your digital security and browsing experience. However, it’s essential to perform a thorough cleanup to ensure that no remnants of the adware remain and that your system is restored to its optimal state.
Clearing Browser Caches and Cookies
Google Chrome
- Click on the three vertical dots in the top-right corner to open the menu.
- Select “History” and then “History” again from the dropdown menu.
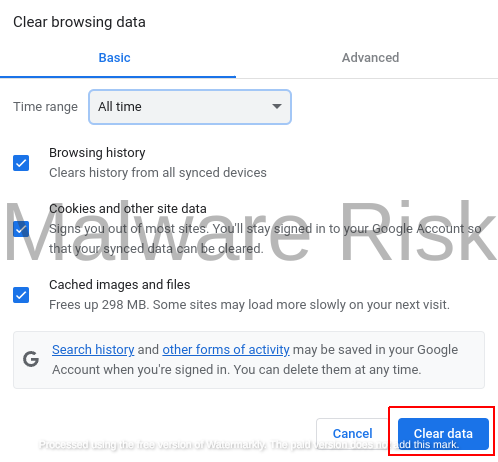
- Click on “Clear browsing data” on the left sidebar.
- Choose the time range and select “Cookies and other site data” and “Cached images and files.”
- Click “Clear data” to remove these items.
Mozilla Firefox
- Click on the three horizontal lines in the top-right corner to open the menu.
- Select “Settings” and go to the “Privacy & Security” tab.
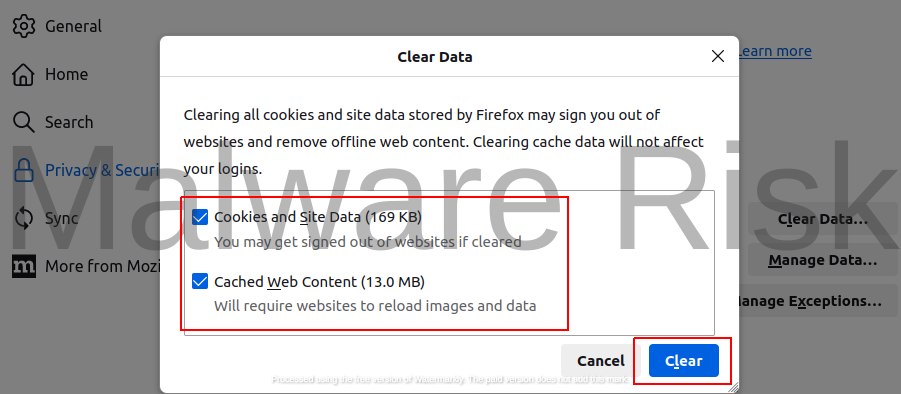
- Under “Cookies and Site Data,” click on “Clear Data.“
- Check both “Cookies and Site Data” and “Cached Web Content” and click “Clear.“
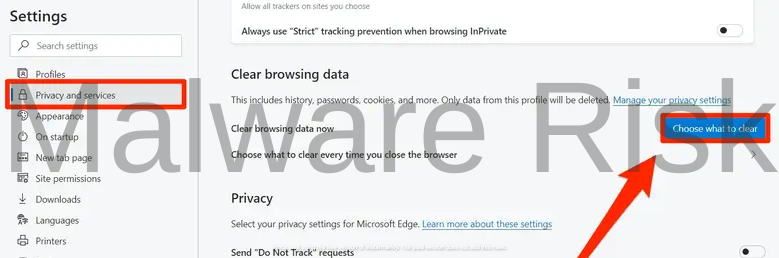
Microsoft Edge
- Click on the three horizontal dots in the top-right corner to open the menu.
- Select “Settings” and scroll down to “Privacy, search, and services.“
- Click on “Choose what to clear” under “Clear browsing data.“
- Check “Cookies and other site data” and “Cached images and files,” then click “Clear.“
Scanning for Leftover Files and Registry Entries
Check Program Files
- Navigate to “C:\Program Files” (or “C:\Program Files (x86)” for 32-bit applications on a 64-bit system).
- Look for folders related to the adware and delete them.

Run Disk Cleanup
- Type “Disk Cleanup” in the Windows search bar and select the app.
- Choose the drive where your operating system is installed (usually “C:“) and click “OK.“
- Check all the boxes, including “Temporary files” and “System error memory dump files,” and click “OK” to clean up unnecessary files.

Resetting Browser Settings to Default
Google Chrome
- Open Chrome, click on the three vertical dots, and select “Settings.“
- Scroll down and click on “Advanced.“
- Under “Reset and clean up,” click on “Restore settings to their original defaults” and confirm the reset.
Mozilla Firefox
- Open Firefox, click on the three horizontal lines, and select “Help.“
- Choose “Troubleshooting Information.“
- Click “Refresh Firefox” to reset your browser.
Microsoft Edge
- Open Edge, click on the three horizontal dots, and select “Settings.“
- Scroll down and click on “Reset settings.“
- Click “Restore settings to their default values” and confirm the reset.
Completing these cleanup steps ensures that your system is free from any remnants of adware and that your browsers are returned to their default, secure state. It’s an essential part of the adware removal process, helping you maintain a clean and efficient computer environment.
Dealing with Persistent Adware
While removing adware is typically a straightforward process, there are instances where it seems to have a knack for returning, like an unwelcome guest that just won’t leave. Dealing with persistent adware can be frustrating, but there are advanced removal methods and resources that can help you regain control of your computer.
Advanced Removal Methods
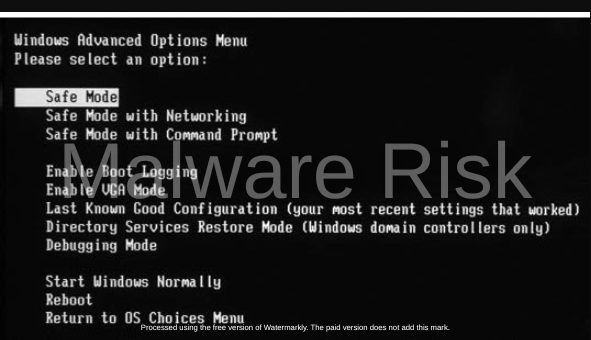
Boot into Safe Mode
Persistent adware may have hidden itself deep within your system, making it resistant to removal in normal mode. Booting your computer into Safe Mode (usually done by pressing F8 or Shift+F8 during startup) can limit the number of processes running and allow for more effective removal.
Use Specialized Removal Tools
Some adware strains are particularly stubborn and may require specialized removal tools. Tools like AdwCleaner, Malwarebytes Anti-Malware, and Spyhunter are designed to target and eliminate persistent adware and other malware.
Manually Inspect System Files
While it’s a more advanced step, manually inspecting system files and folders can help identify and remove adware that has embedded itself deeply. Be cautious during this process, as deleting critical system files can harm your computer’s functionality.
Review System Restore Points
If you have previously created system restore points, consider restoring your computer to a point before the adware infection occurred. This can effectively revert your system to a state where the adware was not present.

Modify Hosts File
Adware may manipulate your computer’s hosts file to control your internet access. Review the hosts file (located in C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc) and remove any suspicious entries. Be cautious while editing this file, as incorrect changes can affect your internet connectivity.

Seeking Help from Experts or Forums
If persistent adware continues to evade your removal efforts, seeking help from experts or online forums can be invaluable. Here are some steps to consider:
- Contact Technical Support: If your computer is under warranty or you have a tech support service, reach out to them for assistance. They may be able to guide you through the removal process or offer remote support.
- Online Tech Forums: Many tech forums have dedicated sections for malware removal. Websites like BleepingComputer and Malwarebytes have communities of experts who can help you diagnose and remove adware. Provide as much information as possible about your issue when seeking help.
Professional Malware Removal Services
In extreme cases, consider enlisting the help of professional malware removal services. These experts specialize in removing even the most stubborn adware and malware infections. Be prepared to pay for their services, but it can be a worthwhile investment for regaining control of your computer.
Backup and Reinstall
If all else fails, and your computer remains compromised, the most drastic solution is to back up your important data and perform a clean reinstall of your operating system. This ensures the complete removal of adware, but it’s a time-consuming process.

Dealing with persistent adware can be challenging, but with persistence and the right resources, you can regain control of your computer. Remember to maintain safe browsing habits and keep your security software up-to-date to minimize the risk of future adware infections.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, adware infections remain a persistent concern for computer users. They not only disrupt our online experience with incessant ads but can also pose significant security risks. This comprehensive guide has equipped you with the knowledge and tools to combat adware effectively.
Understanding the nature of adware, its infiltration tactics, and the motivations behind its existence is really important. Knowing the risks adware can pose, from privacy invasion to data theft and system instability is also crucial. Prevention strategies have been discussed here, emphasizing safe browsing habits, cautious downloads, software updates, and the use of ad-blockers and security extensions.
You must also know the essential steps of adware removal, from manual removal techniques to leveraging antivirus software. Cleaning up your system after an adware infection is necessary to ensure that no remnants linger.
Finally, for the persistent adware that refuses to go quietly into the night, you may go for advanced removal methods or seek assistance from experts and tech forums.
In the world of computing, vigilance and proactive measures are your best allies against adware and other digital threats. By arming yourself with knowledge and adopting secure practices, you can maintain a clean and secure digital environment, free from the clutches of adware’s unwelcome presence. Stay safe, stay secure, and enjoy a hassle-free online experience. If you notice something wrong in the steps or article, Click here to suggest an edit.

Nishant Verma is a senior web developer who love to share his knowledge about Linux, SysAdmin, and more other web handlers. Currently, he loves to write as content contributor for ServoNode and also collaborated with MRLabs now.

