Acquiring basic knowledge about the ever-looming cyber threat of ransomware, its consequences, and effective techniques to combat its intrusion is fundamentally important in today’s data-driven society. Ransomware can be a considerable threat to your privacy, data security, and even financial resources. This complex malicious software comes in different forms and infiltrates your computer in various sub-cloak ways that hardly raise suspicion. The capacity to identify ransomware, understand it, and effectively use antivirus and anti-malware software not only ensures your data protection but also develops essential digital literacy. By delving deep into advanced ransomware removal techniques and future-proof preventive strategies, you can safeguard your digital world, leading to a more secure virtual environment.
Quick Links
Understanding Ransomware
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a harmful type of malware, short for malicious software, that encrypts a victim’s files. The attacker then demands a ransom from the victim to restore access to the data on payment. Criminals often use ransomware to exploit and inflict major damage on data-driven elements of society by targeting individual users, small to large businesses, and even government systems.
Types of Ransomware
There are two major types of ransomware: crypto ransomware and locker ransomware. Crypto ransomware encrypts valuable files on a computer so the victim cannot access them, then demands a ransom to decrypt these files. Locker ransomware locks the victim completely out of their device, barring access to all files, applications, and services on the device until the victim pays a ransom. Though they operate differently, both types aim to extort money from victims through denial of access to personal data.
How Ransomware Infects Computers
Ransomware can infect computers in several ways. A common method is through malicious spam (malspam) where unsolicited emails trick users into opening attachments or clicking links that infect their computers. Other ways include exploitation of software vulnerabilities, internet traffic redirects to malicious websites, and even through portable storage devices. Increasingly, social engineering methods like phishing or impersonation are used, tricking users into granting the malware access.
The Damage Caused by Ransomware

The damage caused by ransomware can range from minor inconveniences to catastrophic loss. In many instances, ransomware can result in the permanent loss of personal or corporate data. Businesses may need to halt operations or even shut down due to the inability to access critical data. The potential damage also extends beyond the immediate loss of access to files. Breached data could include sensitive customer information, the exposure of which could lead to reputational damage, litigation, and regulatory fines. This not only has financial implications but can also cause distrust among customers, partners, and other stakeholders. In the case of healthcare systems or government agencies, the impact of ransomware could have life-threatening consequences when access to critical services is blocked.
Identifying Ransomware
Detecting Signs of Ransomware
Ransomware, a form of malware, can invade your computer and encrypt your data, holding it hostage until a ransom is paid. It’s crucial to recognize the signs of a ransomware infection promptly to mitigate damage and protect your information.
An unexpected encryption of your important files is the most operationally crippling sign of ransomware. Typically, you’ll be unable to access your files, and they might have different extensions or names. Check for files with unusual or unfamiliar extensions as well as files that give a decryption instruction.
Noticing Suspicious Activities
Pay attention to any strange pop-ups or system warnings. These messages often indicate a ransomware infection. For example, an unusual pop-up might inform you that your files are encrypted and demand a ransom for decryption. A ransom note is a clear indication that you’re dealing with ransomware. This note usually includes instructions on how to pay the ransom in cryptocurrency and might threaten to delete files if the ransom isn’t paid.
Observing Unusual System Behavior
Apart from the above-mentioned signs, it is also crucial to monitor your computer’s behavior. Ransomware often causes your system to act erratically. For instance, your computer might slow down dramatically, as the ransomware uses system resources to encrypt your files.

Additionally, your antivirus software might continually flag or quarantine certain files, or you may notice new icons on your desktop that weren’t there before. Applications may freeze or crash frequently, and your computer might restart on its own. Keep an eye out for these behaviors as they might indicate a ransomware infection.
Applying these enhanced observation skills and understanding the clear signs of a ransomware attack can help in the early detection and prompt response to these threats. This can significantly reduce the potential impact, damage, and cost associated with these cyber-attacks.
Using Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
The Role of Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Both antivirus and anti-malware software play crucial roles in detecting and neutralizing a ransomware attack. While antivirus programs primarily help to detect traditional viruses, they may also recognize well-known ransomware threats. In contrast, anti-malware software is explicitly designed to tackle sophisticated malware threats, including ransomware.

Antivirus Software Options
Numerous antivirus software options can help combat ransomware. Norton Antivirus and McAfee Antivirus are two common options that have special features to counteract ransomware. They perform regular system scans, detect potential threats, and remove them before they can cause damage. You only need to download the software, install it, and run the recommended security scans. Remember to promptly update the software when updates are available to ensure optimal performance.
Anti-Malware Software Options
The most popular anti-malware software includes Malwarebytes, Spyhunter, Combo Cleaner and Bitdefender. These tools focus more on cutting-edge threats like ransomware or zero-day exploits, which are new forms of malware not yet recognized by antivirus databases. These software programs also need to be downloaded, installed, and regularly updated. They offer the option to run system scans that detect and remove ransomware.
Operating Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Using antivirus and anti-Malware software is reasonably straightforward. After installation, set up the program to run automatic scans regularly. You can manually run a scan by opening the program, selecting ‘scan,’ and choosing the type of scan you want to perform. Performing regular updates is crucial to ensure the software has the newest virus and malware definitions.
Limitations and Benefits of Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
While antivirus and anti-malware software provide robust protection against known threats, they cannot stop all malware. New forms of malware or less common types may slip through the cracks. Furthermore, they won’t protect against user error, such as if you actively download a malicious file.
However, the benefits of these software applications far outweigh their limitations. They offer real-time protection, scanning all files that you access or download, and provide an extra layer of security, helping you to prevent potential data and financial losses.
Preventive Measures against Ransomware
Though antivirus and anti-malware software significantly reduce the risk of ransomware, it’s always better to prevent attacks. Be cautious when clicking links or downloading files from unknown sources, regularly update your system and software to patch potential security holes, and perform frequent backups of important data. With these preventative measures in place, you’ll reduce the likelihood of falling victim to a ransomware attack.
Advanced Ransomware Removal Techniques
Understanding Ransomware and Its Removal
Ransomware is a form of malware that encrypts a victim’s files. The attacker then demands a ransom from the victim to restore access to the data upon payment. However, victims should never pay the ransom as it encourages the offenders and there’s no guarantee that access will be restored. Advanced ransomware removal techniques can help you regain access to your system.
Making Use of Ransomware Decryptor Tools
Ransomware Decryptor tools are specialized programs that help decrypt files encrypted by specific ransomware. Notably, different decryptor tools correspond to different types of ransomware, so it is crucial to identify the type of ransomware infecting your system before choosing the appropriate tool. Kaspersky Lab, AVG, Avast, Emsisoft are among many organizations that offer free decryptor tools.
Once you’ve identified your type of Ransomware, search for a specific Ransomware Decryptor Tool from a trusted source like Kaspersky, AVG, or Avast. Be cautious, only download from official sources to avoid further infections.
Run the tool. Most Decryptor programs will provide on-screen instructions to guide you through the process. These tools will analyze your files and apply the necessary decryption keys where possible.
Using Windows System Restore Feature
If a recent system restore point is present, you can use the Windows System Restore feature to recover your system to a point before the ransomware attack. This method can effectively nullify the ransomware infection, but will erase any system changes made after the selected restore point.
Boot your computer in Safe mode by restarting your computer and pressing the F8 key before the Windows logo appears. From the boot menu, select ‘Safe Mode with Command Prompt’.
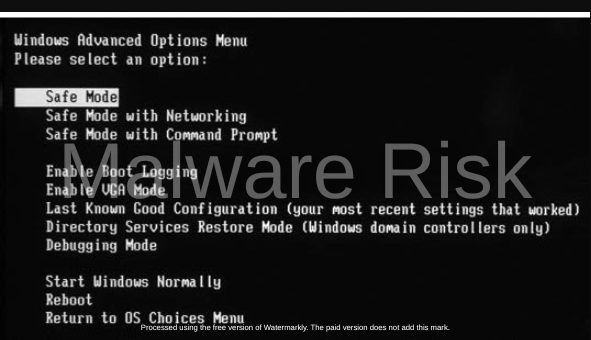
When the Command Prompt appears, type ‘cd restore’ and press Enter. Next, type ‘rstrui.exe’ and press Enter again.

The system restore window should appear. Click ‘Next’, then select a restore point before the infection occurred and click ‘Next’ again. Follow the on-screen instructions to restore your system.
Advanced Anti-Malware Scanning
In case previous methods didn’t work, advance anti-malware tools are effective for removing stubborn ransomware. Examples of such tools include Spyhunter, Combo Cleaner, MalwareBytes, and Emsisoft Emergency Kit.
- Download the anti-malware tool.
- Boot your computer into safe mode, then run the downloaded program. Follow the prompts to install it.
- Once the tool is installed, perform a “deep scan” or “full scan” for maximum effect.
These advanced approaches to ransomware removal require some technical acumen, particularly when navigating system restore options or handling decryption tools. Regularly updating software, maintaining strong, unique passwords, and not clicking on suspicious emails or links can prevent ransomware attacks in the first place.
Preventing Future Ransomware Attacks
Regular Updates: Maintaining a Healthy Computer System
Regular updates for your operating system, anti-virus software, and other critical programs play an important role in preventing ransomware attacks. These updates often include patches for identified vulnerabilities that ransomware could exploit. Enabling automatic updates can ensure your computer always has the latest protection.

Creating Strong Passwords: Your First Line of Defense
Utilizing strong passwords is another key preventative measure. Try to avoid obvious choices like “password1″ or “1234”. A strong password should be a complex combination of letters, numbers and special characters. Change your passwords periodically and avoid using the same password across different platforms.
Leveraging Multi-factor Authentication for Extra Security
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring two or more pieces of evidence before granting account access. This could be something you know (like a password), something you have (like a physical token or phone), or something you are (like a fingerprint). Most popular services provide MFA options, so it’s a matter of taking the time to enable and use them.
Following Secure Online Practices: Minimize Exposure to Threats
Secure online practices help to reduce the risk of future ransomware attacks. Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources. If a message seems suspicious, even if you know the person who sent it, it’s best to delete it without opening it. Regularly back up your data to an external drive or cloud-based service. If your computer becomes infected with ransomware, you’ll have up-to-date copies of your files and won’t be compelled to pay a ransom.
Installing Anti-ransomware Software: A Proactive Approach
There are software tools specifically designed to protect against ransomware attacks. These tools can detect and block attempted ransomware infections before they infiltrate your system. Moreover, they can provide regular system scans to identify potential vulnerabilities.
Understanding Social Engineering: Don’t Fall for Traps
Ransomware often relies on tricking individuals into clicking on malicious links or downloading infected files. This is known as social engineering. Understanding these tactics can help you avoid falling for them. Don’t respond to emails asking for personal information, be wary of pop-up windows claiming you won a prize, and avoid unsolicited communications from strangers.
By adopting these practices, you’ll be able to reduce the risk of falling victim to future ransomware attacks. Remember, prevention is always better than cure when it comes to cyber threats.
Conclusion
The digital world will continue its upward trajectory of intertwining with our day-to-day life, making it crucial to secure our virtual space. Equipping oneself with the knowledge to identify and remove ransomware, apply advanced techniques, and enforce preventive measures can fundamentally align you with optimal cybersecurity practices. Utilize your understanding of ransomware and anti-malware software operation to resist this cyber threat. Reducing the risk of future attacks by employing preventive measures and secure online practices is equally important. The technological landscape continues to evolve, bringing with it various challenges, but armed with the right knowledge and tools, you gain the power to protect what you value most on your computer. If you notice something wrong in the steps or article, Click here to suggest

Nishant Verma is a senior web developer who love to share his knowledge about Linux, SysAdmin, and more other web handlers. Currently, he loves to write as content contributor for ServoNode and also collaborated with MRLabs now.

